A product manager plays a crucial role in defining the strategy, roadmap, and features of a product. This role involves understanding customer needs, analyzing market trends, and aligning the product vision with business goals. As the key driver of product success, a product manager bridges the gap between various departments such as engineering, marketing, sales, and customer support.
By leading cross-functional teams, a product manager ensures the product delivers unique value and drives company growth. The role involves constant evaluation of market conditions, competition, and customer feedback to shape the product’s future direction.
Effective product management requires not only a deep understanding of the product but also a strategic mindset to prioritize features and plan releases that meet both customer and business needs.
Product managers must also balance stakeholder expectations, making tough decisions about which features to prioritize based on the value they bring to the product. Ultimately, their role is to guide the product’s lifecycle from concept to launch and beyond, ensuring its continued success and alignment with market demands.
What Does a Product Manager Do?
A product manager is at the heart of a product’s success. By setting the strategy, defining the roadmap, and prioritizing features, product managers ensure the product delivers value to both customers and the business. This role is inherently cross-functional, requiring collaboration with teams like engineering, marketing, and sales.
Product managers create a clear vision that aligns with business goals, making strategic decisions that influence the product’s growth and development. They also analyze the market and competition, keeping the product ahead in a dynamic landscape.
Product Manager Responsibilities
While the responsibilities of a product manager vary, they generally focus on six key areas:
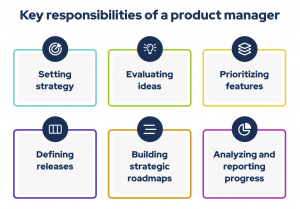
1. Setting Strategy
At the highest level, product managers define the product’s vision and strategic direction. By crafting a clear business case, they connect each initiative or feature back to the product’s goals. This clarity helps teams understand why they are building something and where it fits within the larger product vision.
Strategic planning involves determining major areas of investment to prioritize goals effectively. Product managers also own the product roadmap—a visual representation of what will be delivered and when.
2. Evaluating Ideas
Product managers oversee the idea management process, gathering input from customers, internal teams, and stakeholders. They curate ideas that add value to customers, ensuring that each idea is integrated into the product’s development lifecycle. This includes maintaining feedback loops to communicate progress and decisions back to key contributors.
3. Prioritizing Features
Balancing customer needs with business objectives, product managers prioritize features by ranking them based on their strategic value. They collaborate with engineering on technical specifications and work with cross-functional teams to ensure that products are delivered with all necessary components. Product managers rely on value-based product development to focus on delivering high-impact features with minimal effort.
4. Defining Releases
Product managers translate strategy into actionable work by defining what the team will build and setting release schedules. They manage the release process, bridging the gaps between marketing, sales, and customer support. This cross-functional alignment is key to a successful product launch.
5. Building and Sharing Strategic Roadmaps
A product roadmap is a vital communication tool for product managers. It helps align teams and tracks progress toward business objectives. Different types of roadmaps serve different audiences—executives need high-level insights, while engineering teams need to focus on timelines and sequencing.
6. Analyzing and Reporting on Progress
Product managers are laser-focused on results. They monitor team performance, track progress toward product goals, and analyze product usage. This requires understanding both quantitative and qualitative data. By using tools like sprint burndown charts and adoption reports, product managers can ensure the product remains on track to meet customer and business needs.
Tips for New Product Managers
1. Start with Strategy
Root each decision in strategy. Familiarize yourself with the product’s existing goals, then develop a clear framework that aligns with business needs.
2. Get to Know Your Customers
Empathy is essential for success. Understand your customers’ problems by engaging directly with them, whether through sales calls, meetings, or data analysis.
3. Build Relationships with Your Team
Collaboration is key. Strong connections with engineers, designers, marketers, and salespeople will foster trust and enable smoother product development processes.
4. Learn to Say No
Product managers are often inundated with requests. Learning to say “no” or “not now” is essential to keeping the product focused and aligned with strategic goals.
5. Be Patient with Yourself
It takes time to grow into the role of a product manager. Embrace a learning mindset and be prepared to iterate and improve continuously.
FAQs About the Product Manager Role
1. How Do You Start a Career in Product Management?
Many product managers begin in adjacent roles like customer support or product marketing. Gaining experience in understanding the business, product, and customers is key to transitioning into product management.
2. What is the Difference Between a Product Manager and a Project Manager?
While product managers focus on product strategy and customer needs, project managers ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. The former owns the product’s vision; the latter manages the execution of tasks related to that vision.
 Pin
Pin3. Which Tools Do Product Managers Use?
Product managers use various tools like roadmapping software, customer feedback platforms, and project management systems. These help streamline workflows, align teams, and track progress.